WACV 2025 Paper
Kevin Flanagan, Dima Damen, Michael Wray
University of Bristol
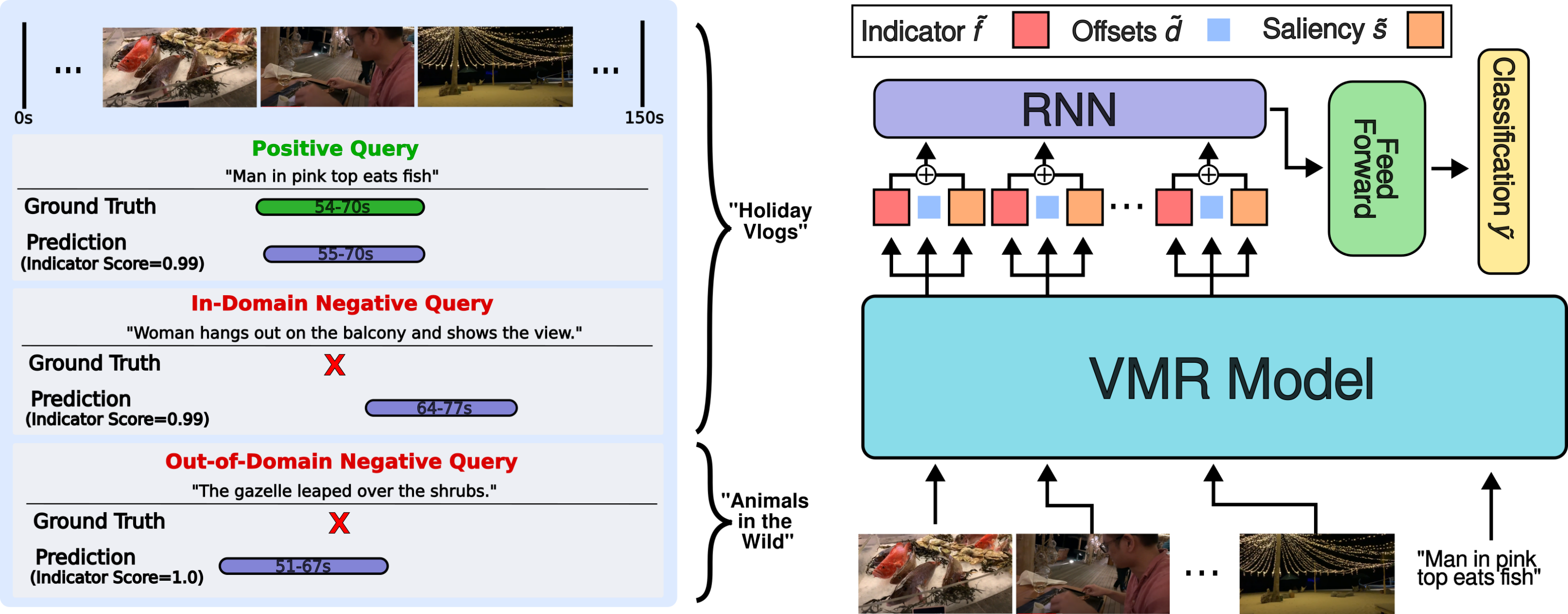 Video moment retrieval models are designed to predict start and end times in a video given a query sentence, regardless of whether the moment actually exists. We alter existing moment retrieval models to be capable of rejecting query sentences which do not correspond to a moment in the video.
Video moment retrieval models are designed to predict start and end times in a video given a query sentence, regardless of whether the moment actually exists. We alter existing moment retrieval models to be capable of rejecting query sentences which do not correspond to a moment in the video.
Abstract
Video Moment Retrieval is a common task to evaluate the performance of visual-language models—it involves localising start and end times of moments in videos from query sentences. The current task formulation assumes that the queried moment is present in the video, resulting in false positive moment predictions when irrelevant query sentences are provided. In this paper we propose the task of Negative-Aware Video Moment Retrieval (NA-VMR), which considers both moment retrieval accuracy and negative query rejection accuracy. We make the distinction between In-Domain and Out-of-Domain negative queries and provide new evaluation benchmarks for two popular video moment retrieval datasets: QVHighlights and Charades-STA. We analyse the ability of current SOTA video moment retrieval approaches to adapt to Negative-Aware Video Moment Retrieval and propose UniVTG-NA, an adaptation of UniVTG designed to tackle NA-VMR. UniVTG-NA achieves high negative rejection accuracy (avg. 98.4%) scores while retaining moment retrieval scores to within 3.87% Recall@1 0.5 IoU.
Video
Paper
Code, Data Splits and Features
The dataset splits and code for UniVTG-NA can be found here
Bibtex
@InProceedings{flanagan2025moment,
author ={Flanagan, Kevin and Damen, Dima and Wray, Michael},
title ={Moment of Untruth: Dealing with Negative Queries in Video Moment Retrieval},
booktitle ={Winter Applications of Computer Vision Conference (WACV)},
year ={2025}
}
Acknowledgements
K Flanagan is supported by UKRI (Grant ref EP/S022937/1) CDT in Interactive AI & Qinetiq Ltd via studentship CON11954. D Damen is supported by EPSRC Fellowship UMPIRE (EP/T004991/1) & EPSRC Program Grant Visual AI (EP/T028572/1)